/// LSU EE 4702-1 (Fall 2017), GPU Programming
//
/// Simple Demo of Point Masses and Springs
/// Version used in class 28 August 2017, when we made setup 3 arrange
/// the balls in a spiral.
/// Purpose
//
// Demonstrate simulation of string modeled as point masses and springs
/// What Code Does
// Simulates a string of beads over a platform. The string is modeled
// as point masses connected by springs with a long relaxed
// length. The platform consists of tiles, some are purple-tinted
// mirrors (showing a reflection of the ball), the others show the
// course syllabus.
/// Keyboard Commands
//
/// Object (Eye, Light, Ball) Location or Push
// Arrows, Page Up, Page Down
// Move object or push ball, depending on mode.
// With shift key pressed, motion is 5x faster.
// 'e': Move eye.
// 'l': Move light.
// 'b': Move head (first) ball. (Change position but not velocity.)
// 'B': Push head ball. (Add velocity.)
//
/// Eye Direction
// Home, End, Delete, Insert
// Turn the eye direction.
// Home should rotate eye direction up, End should rotate eye
// down, Delete should rotate eye left, Insert should rotate eye
// right. The eye direction vector is displayed in the upper left.
/// Simulation Options
// (Also see variables below.)
//
// '1' Set up scene 1.
// '2' Set up scene 2.
// 'p' Pause simulation. (Press again to resume.)
// ' ' (Space bar.) Advance simulation by 1/30 second.
// 'S- ' (Shift-space bar.) Advance simulation by one time step.
// 'h' Freeze position of first (head) ball. (Press again to release.)
// 't' Freeze position of last (tail) ball. (Press again to release.)
// 's' Stop balls.
// 'g' Turn gravity on and off.
// 'F12' Write screenshot to file.
/// Variables
// Selected program variables can be modified using the keyboard.
// Use "Tab" to cycle through the variable to be modified, the
// name of the variable is displayed next to "VAR" on the bottom
// line of green text.
// 'Tab' Cycle to next variable.
// '`' Cycle to previous variable.
// '+' Increase variable value.
// '-' Decrease variable value.
//
// VAR Spring Constant - Set spring constant.
// VAR Air Resistance - Set air resistance.
// VAR Light Intensity - The light intensity.
// VAR Gravity - Gravitational acceleration. (Turn on/off using 'g'.)
#define GL_GLEXT_PROTOTYPES
#define GLX_GLXEXT_PROTOTYPES
#include <GL/gl.h>
#include <GL/glext.h>
#include <GL/glx.h>
#include <GL/glxext.h>
#include <GL/glu.h>
#include <GL/freeglut.h>
#include <gp/util.h>
#include <gp/glextfuncs.h>
#include <gp/coord.h>
#include <gp/shader.h>
#include <gp/pstring.h>
#include <gp/misc.h>
#include <gp/gl-buffer.h>
#include <gp/texture-util.h>
#include "shapes.h"
///
/// Main Data Structures
///
//
// class World: All data about scene.
class World;
// Object Holding Ball State
//
class Ball {
public:
pCoor position;
pVect velocity;
float mass;
float radius;
bool contact; // Can be used for special effects.
void push(pVect amt);
void translate(pVect amt);
void stop();
void freeze();
};
#include "demo-2-springs-graphics.cc"
void
World::init()
{
chain_length = 20;
balls = new Ball[chain_length];
distance_relaxed = 15.0 / chain_length;
opt_spring_constant = 1000;
variable_control.insert(opt_spring_constant,"Spring Constant");
opt_gravity_accel = 9.8;
opt_gravity = true;
gravity_accel = pVect(0,-opt_gravity_accel,0);
variable_control.insert(opt_gravity_accel,"Gravity");
opt_time_step_easy = false;
opt_air_resistance = 0.001;
variable_control.insert(opt_air_resistance,"Air Resistance");
world_time = 0;
time_step_count = 0;
last_frame_wall_time = time_wall_fp();
frame_timer.work_unit_set("Steps / s");
init_graphics();
ball_setup_2();
}
///
/// Physical Simulation Code
///
/// Initialize Simulation
//
void
World::ball_setup_1()
{
/// Arrange balls vertically.
// Desired position of bottom ball.
//
pCoor bottom_pos(12.5,distance_relaxed,-13.7);
// Desired distance between adjacent balls.
//
pVect ball_separation(0, distance_relaxed, 0); // Points up.
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[chain_length-i-1];
ball->position = bottom_pos + i * ball_separation;
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
ball->radius = 0.3 * distance_relaxed;
ball->mass = 4/3.0 * M_PI * pow(ball->radius,3);
ball->contact = false;
}
opt_head_lock = true;
}
void
World::ball_setup_2()
{
/// Arrange and size balls to form a pendulum.
// Desired position of first ball.
//
pCoor first_ball_pos(13.4,17.8,-9.2);
// Desired distance between adjacent balls.
//
pVect ball_separation(distance_relaxed, 0, 0); // Points in +x direction.
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
ball->position = first_ball_pos + i * ball_separation;
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
ball->radius = ( i == chain_length - 1 ? 0.6 : 0.3 ) * distance_relaxed;
ball->mass = 4/3.0 * M_PI * pow(ball->radius,3);
ball->contact = false;
}
opt_head_lock = true;
}
void
World::ball_setup_3()
{
/// Arrange and size balls to form a spiral.
//
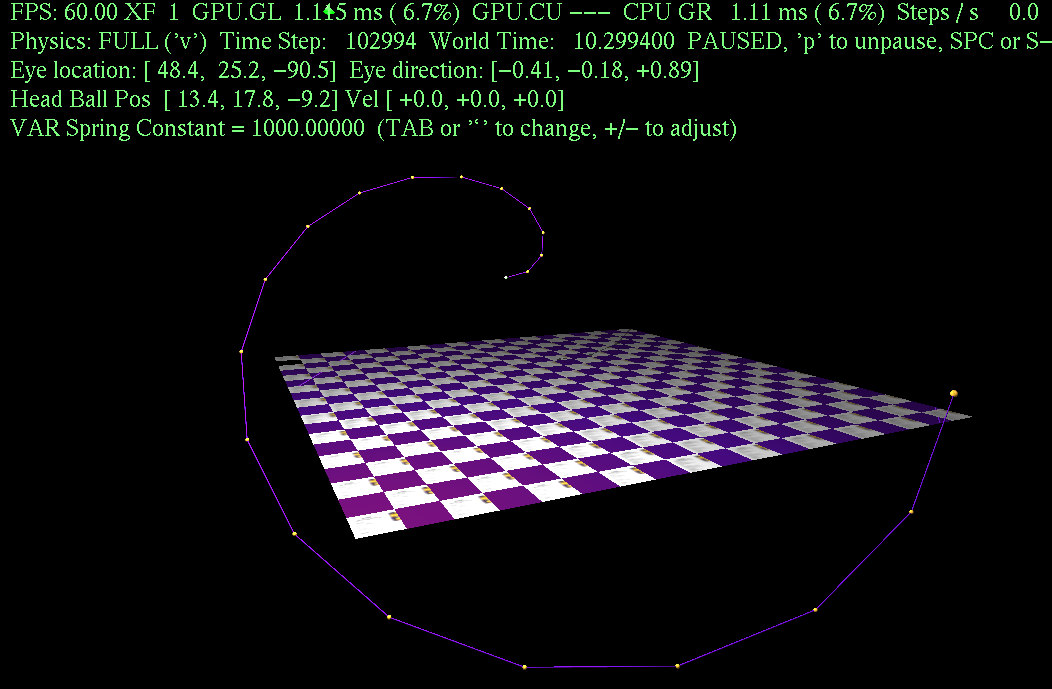 // Desired position of first ball.
//
pCoor first_ball_pos(13.4,17.8,-9.2);
pVect peu(first_ball_pos,eye_location);
pNorm pe = peu;
pNorm uz = pe + pVect(0,1,0);
pNorm ux = cross( pVect(0,1,0), uz );
pNorm uy = cross( uz, ux );
float r = 10;
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
double theta = 2 * M_PI * i / chain_length;
// ball->position.x = r * theta * cos(theta);
// ball->position.y = r * theta * sin(theta);
ball->position = first_ball_pos
+ r * theta * cos(theta) * ux
+ r * theta * sin(theta) * uy;
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
ball->radius = ( i == chain_length - 1 ? 0.6 : 0.3 ) * distance_relaxed;
ball->mass = 4/3.0 * M_PI * pow(ball->radius,3);
ball->contact = false;
}
opt_head_lock = true;
}
void
World::ball_setup_4()
{
}
void
World::ball_setup_5()
{
}
/// Advance Simulation State by delta_t Seconds
//
void
World::time_step_cpu_easy(double delta_t)
{
time_step_count++;
//
/// Compute force and update velocity of each ball.
//
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Skip locked balls.
//
if ( opt_head_lock && i == 0 || opt_tail_lock && i == chain_length - 1 )
{
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
continue;
}
pVect force(0,0,0);
// Gravitational Force
//
force += ball->mass * gravity_accel;
//
// Newton's most famous equation.
// Spring Force from Neighbor Balls
//
for ( int direction: { -1, +1 } )
{
const int n_idx = i + direction; // Compute neighbor index.
// Skip this neighbor if neighbor doesn't exit.
//
if ( n_idx < 0 ) continue;
if ( n_idx == chain_length ) continue;
Ball* const neighbor_ball = &balls[n_idx];
// Construct a normalized (Unit) Vector from ball to neighbor.
//
pNorm ball_to_neighbor( ball->position, neighbor_ball->position );
// Get distance between balls using pNorm member magnitude.
//
const float distance_between_balls = ball_to_neighbor.magnitude;
// Compute by how much the spring is stretched (positive value)
// or compressed (negative value).
//
const float spring_stretch =
distance_between_balls - distance_relaxed;
// Add on the force due to the neighbor_ball.
//
force += opt_spring_constant * spring_stretch * ball_to_neighbor;
// h ( l - l_r ) u_12
//
// Comments above show symbols used in notes.
}
// Update Velocity
//
// This code assumes that force on ball is constant over time
// step. This is clearly wrong when balls are moving with
// respect to each other because the springs are changing
// length. This inaccuracy will make the simulation unstable
// when spring constant is large for the time step.
//
ball->velocity += ( force / ball->mass ) * delta_t;
// Air Resistance
//
const double fs = pow(1+opt_air_resistance,-delta_t);
ball->velocity *= fs;
}
///
/// Update Position of Each Ball
///
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Update Position
//
// Assume that velocity is constant.
//
ball->position += ball->velocity * delta_t;
// Possible Collision with Platform
//
// Skip if collision impossible.
//
if ( !platform_collision_possible(ball->position) ) continue;
if ( ball->position.y >= 0 ) continue;
// Reflect y (vertical) component of velocity, with a reduction
// due to energy lost in the collision.
//
if ( ball->velocity.y < 0 )
ball->velocity.y = - 0.9 * ball->velocity.y;
}
}
void
World::time_step_cpu_full(double delta_t)
{
time_step_count++;
//
/// Compute force and update velocity of each ball.
//
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Skip locked balls.
//
if ( opt_head_lock && i == 0 || opt_tail_lock && i == chain_length - 1 )
{
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
continue;
}
pVect force(0,0,0);
// Gravitational Force
//
force += ball->mass * gravity_accel;
// Spring Force from Neighbor Balls
//
for ( int direction: { -1, +1 } )
{
const int n_idx = i + direction; // Compute neighbor index.
if ( n_idx < 0 ) continue;
if ( n_idx == chain_length ) break;
Ball* const neighbor_ball = &balls[n_idx];
// Construct a normalized (Unit) Vector from ball to neighbor.
//
pNorm ball_to_neighbor( ball->position, neighbor_ball->position );
// Get distance between balls using pNorm member magnitude.
//
const float distance_between_balls = ball_to_neighbor.magnitude;
// Compute by how much the spring is stretched (positive value)
// or compressed (negative value).
//
const float spring_stretch =
distance_between_balls - distance_relaxed;
// Compute the speed of ball towards neighbor_ball.
//
pVect delta_v = neighbor_ball->velocity - ball->velocity;
float delta_s = dot( delta_v, ball_to_neighbor );
// Determine whether spring is gaining energy (whether its length
// is getting further from its relaxed length).
//
const bool gaining_e = ( delta_s > 0.0 ) == ( spring_stretch > 0 );
// Use a smaller spring constant when spring is loosing energy,
// a quick and dirty way of simulating energy loss due to spring
// friction.
//
const float spring_constant =
gaining_e ? opt_spring_constant : opt_spring_constant * 0.7;
force += spring_constant * spring_stretch * ball_to_neighbor;
}
// Update Velocity
//
// This code assumes that force on ball is constant over time
// step. This is clearly wrong when balls are moving with
// respect to each other because the springs are changing
// length. This inaccuracy will make the simulation unstable
// when spring constant is large for the time step.
//
ball->velocity += ( force / ball->mass ) * delta_t;
// Air Resistance
//
const double fs = pow(1+opt_air_resistance,-delta_t);
ball->velocity *= fs;
}
///
/// Update Position of Each Ball
///
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Update Position
//
// Assume that velocity is constant.
//
ball->position += ball->velocity * delta_t;
// Possible Collision with Platform
//
// Skip if collision impossible.
//
if ( !platform_collision_possible(ball->position) ) continue;
if ( ball->position.y >= 0 ) continue;
// Snap ball position to surface.
//
ball->position.y = 0;
// Reflect y (vertical) component of velocity, with a reduction
// due to energy lost in the collision.
//
if ( ball->velocity.y < 0 )
ball->velocity.y = - 0.9 * ball->velocity.y;
}
}
bool
World::platform_collision_possible(pCoor pos)
{
// Assuming no motion in x or z axes.
//
return pos.x >= platform_xmin && pos.x <= platform_xmax
&& pos.z >= platform_zmin && pos.z <= platform_zmax;
}
/// External Modifications to State
//
// These allow the user to play with state while simulation
// running.
// Move the ball.
//
void Ball::translate(pVect amt) {position += amt;}
// Add velocity to the ball.
//
void Ball::push(pVect amt) {velocity += amt;}
// Set the velocity to zero.
//
void Ball::stop() {velocity = pVect(0,0,0); }
// Set the velocity and rotation (not yet supported) to zero.
//
void Ball::freeze() {velocity = pVect(0,0,0); }
void World::balls_translate(pVect amt,int b){balls[b].translate(amt);}
void World::balls_push(pVect amt,int b){balls[b].push(amt);}
void World::balls_translate(pVect amt)
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].translate(amt);}
void World::balls_push(pVect amt)
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].push(amt);}
void World::balls_stop()
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].stop();}
void World::balls_freeze(){balls_stop();}
void
World::frame_callback()
{
// This routine called whenever window needs to be updated.
const double time_now = time_wall_fp();
if ( !opt_pause || opt_single_frame || opt_single_time_step )
{
/// Advance simulation state.
// Amount of time since the user saw the last frame.
//
const double wall_delta_t = time_now - last_frame_wall_time;
const double time_step_duration = 0.0001;
// Compute amount by which to advance simulation state for this frame.
//
const double duration =
opt_single_time_step ? time_step_duration :
opt_single_frame ? 1/30.0 :
wall_delta_t;
const double world_time_target = world_time + duration;
while ( world_time < world_time_target )
{
if ( opt_time_step_easy )
time_step_cpu_easy(time_step_duration);
else
time_step_cpu_full(time_step_duration);
world_time += time_step_duration;
}
// Reset these, just in case they were set.
//
opt_single_frame = opt_single_time_step = false;
}
last_frame_wall_time = time_now;
render();
}
int
main(int argv, char **argc)
{
pOpenGL_Helper popengl_helper(argv,argc);
World world(popengl_helper);
popengl_helper.rate_set(30);
popengl_helper.display_cb_set(world.frame_callback_w,&world);
}
// Desired position of first ball.
//
pCoor first_ball_pos(13.4,17.8,-9.2);
pVect peu(first_ball_pos,eye_location);
pNorm pe = peu;
pNorm uz = pe + pVect(0,1,0);
pNorm ux = cross( pVect(0,1,0), uz );
pNorm uy = cross( uz, ux );
float r = 10;
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
double theta = 2 * M_PI * i / chain_length;
// ball->position.x = r * theta * cos(theta);
// ball->position.y = r * theta * sin(theta);
ball->position = first_ball_pos
+ r * theta * cos(theta) * ux
+ r * theta * sin(theta) * uy;
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
ball->radius = ( i == chain_length - 1 ? 0.6 : 0.3 ) * distance_relaxed;
ball->mass = 4/3.0 * M_PI * pow(ball->radius,3);
ball->contact = false;
}
opt_head_lock = true;
}
void
World::ball_setup_4()
{
}
void
World::ball_setup_5()
{
}
/// Advance Simulation State by delta_t Seconds
//
void
World::time_step_cpu_easy(double delta_t)
{
time_step_count++;
//
/// Compute force and update velocity of each ball.
//
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Skip locked balls.
//
if ( opt_head_lock && i == 0 || opt_tail_lock && i == chain_length - 1 )
{
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
continue;
}
pVect force(0,0,0);
// Gravitational Force
//
force += ball->mass * gravity_accel;
//
// Newton's most famous equation.
// Spring Force from Neighbor Balls
//
for ( int direction: { -1, +1 } )
{
const int n_idx = i + direction; // Compute neighbor index.
// Skip this neighbor if neighbor doesn't exit.
//
if ( n_idx < 0 ) continue;
if ( n_idx == chain_length ) continue;
Ball* const neighbor_ball = &balls[n_idx];
// Construct a normalized (Unit) Vector from ball to neighbor.
//
pNorm ball_to_neighbor( ball->position, neighbor_ball->position );
// Get distance between balls using pNorm member magnitude.
//
const float distance_between_balls = ball_to_neighbor.magnitude;
// Compute by how much the spring is stretched (positive value)
// or compressed (negative value).
//
const float spring_stretch =
distance_between_balls - distance_relaxed;
// Add on the force due to the neighbor_ball.
//
force += opt_spring_constant * spring_stretch * ball_to_neighbor;
// h ( l - l_r ) u_12
//
// Comments above show symbols used in notes.
}
// Update Velocity
//
// This code assumes that force on ball is constant over time
// step. This is clearly wrong when balls are moving with
// respect to each other because the springs are changing
// length. This inaccuracy will make the simulation unstable
// when spring constant is large for the time step.
//
ball->velocity += ( force / ball->mass ) * delta_t;
// Air Resistance
//
const double fs = pow(1+opt_air_resistance,-delta_t);
ball->velocity *= fs;
}
///
/// Update Position of Each Ball
///
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Update Position
//
// Assume that velocity is constant.
//
ball->position += ball->velocity * delta_t;
// Possible Collision with Platform
//
// Skip if collision impossible.
//
if ( !platform_collision_possible(ball->position) ) continue;
if ( ball->position.y >= 0 ) continue;
// Reflect y (vertical) component of velocity, with a reduction
// due to energy lost in the collision.
//
if ( ball->velocity.y < 0 )
ball->velocity.y = - 0.9 * ball->velocity.y;
}
}
void
World::time_step_cpu_full(double delta_t)
{
time_step_count++;
//
/// Compute force and update velocity of each ball.
//
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Skip locked balls.
//
if ( opt_head_lock && i == 0 || opt_tail_lock && i == chain_length - 1 )
{
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
continue;
}
pVect force(0,0,0);
// Gravitational Force
//
force += ball->mass * gravity_accel;
// Spring Force from Neighbor Balls
//
for ( int direction: { -1, +1 } )
{
const int n_idx = i + direction; // Compute neighbor index.
if ( n_idx < 0 ) continue;
if ( n_idx == chain_length ) break;
Ball* const neighbor_ball = &balls[n_idx];
// Construct a normalized (Unit) Vector from ball to neighbor.
//
pNorm ball_to_neighbor( ball->position, neighbor_ball->position );
// Get distance between balls using pNorm member magnitude.
//
const float distance_between_balls = ball_to_neighbor.magnitude;
// Compute by how much the spring is stretched (positive value)
// or compressed (negative value).
//
const float spring_stretch =
distance_between_balls - distance_relaxed;
// Compute the speed of ball towards neighbor_ball.
//
pVect delta_v = neighbor_ball->velocity - ball->velocity;
float delta_s = dot( delta_v, ball_to_neighbor );
// Determine whether spring is gaining energy (whether its length
// is getting further from its relaxed length).
//
const bool gaining_e = ( delta_s > 0.0 ) == ( spring_stretch > 0 );
// Use a smaller spring constant when spring is loosing energy,
// a quick and dirty way of simulating energy loss due to spring
// friction.
//
const float spring_constant =
gaining_e ? opt_spring_constant : opt_spring_constant * 0.7;
force += spring_constant * spring_stretch * ball_to_neighbor;
}
// Update Velocity
//
// This code assumes that force on ball is constant over time
// step. This is clearly wrong when balls are moving with
// respect to each other because the springs are changing
// length. This inaccuracy will make the simulation unstable
// when spring constant is large for the time step.
//
ball->velocity += ( force / ball->mass ) * delta_t;
// Air Resistance
//
const double fs = pow(1+opt_air_resistance,-delta_t);
ball->velocity *= fs;
}
///
/// Update Position of Each Ball
///
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Update Position
//
// Assume that velocity is constant.
//
ball->position += ball->velocity * delta_t;
// Possible Collision with Platform
//
// Skip if collision impossible.
//
if ( !platform_collision_possible(ball->position) ) continue;
if ( ball->position.y >= 0 ) continue;
// Snap ball position to surface.
//
ball->position.y = 0;
// Reflect y (vertical) component of velocity, with a reduction
// due to energy lost in the collision.
//
if ( ball->velocity.y < 0 )
ball->velocity.y = - 0.9 * ball->velocity.y;
}
}
bool
World::platform_collision_possible(pCoor pos)
{
// Assuming no motion in x or z axes.
//
return pos.x >= platform_xmin && pos.x <= platform_xmax
&& pos.z >= platform_zmin && pos.z <= platform_zmax;
}
/// External Modifications to State
//
// These allow the user to play with state while simulation
// running.
// Move the ball.
//
void Ball::translate(pVect amt) {position += amt;}
// Add velocity to the ball.
//
void Ball::push(pVect amt) {velocity += amt;}
// Set the velocity to zero.
//
void Ball::stop() {velocity = pVect(0,0,0); }
// Set the velocity and rotation (not yet supported) to zero.
//
void Ball::freeze() {velocity = pVect(0,0,0); }
void World::balls_translate(pVect amt,int b){balls[b].translate(amt);}
void World::balls_push(pVect amt,int b){balls[b].push(amt);}
void World::balls_translate(pVect amt)
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].translate(amt);}
void World::balls_push(pVect amt)
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].push(amt);}
void World::balls_stop()
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].stop();}
void World::balls_freeze(){balls_stop();}
void
World::frame_callback()
{
// This routine called whenever window needs to be updated.
const double time_now = time_wall_fp();
if ( !opt_pause || opt_single_frame || opt_single_time_step )
{
/// Advance simulation state.
// Amount of time since the user saw the last frame.
//
const double wall_delta_t = time_now - last_frame_wall_time;
const double time_step_duration = 0.0001;
// Compute amount by which to advance simulation state for this frame.
//
const double duration =
opt_single_time_step ? time_step_duration :
opt_single_frame ? 1/30.0 :
wall_delta_t;
const double world_time_target = world_time + duration;
while ( world_time < world_time_target )
{
if ( opt_time_step_easy )
time_step_cpu_easy(time_step_duration);
else
time_step_cpu_full(time_step_duration);
world_time += time_step_duration;
}
// Reset these, just in case they were set.
//
opt_single_frame = opt_single_time_step = false;
}
last_frame_wall_time = time_now;
render();
}
int
main(int argv, char **argc)
{
pOpenGL_Helper popengl_helper(argv,argc);
World world(popengl_helper);
popengl_helper.rate_set(30);
popengl_helper.display_cb_set(world.frame_callback_w,&world);
}
 // Desired position of first ball.
//
pCoor first_ball_pos(13.4,17.8,-9.2);
pVect peu(first_ball_pos,eye_location);
pNorm pe = peu;
pNorm uz = pe + pVect(0,1,0);
pNorm ux = cross( pVect(0,1,0), uz );
pNorm uy = cross( uz, ux );
float r = 10;
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
double theta = 2 * M_PI * i / chain_length;
// ball->position.x = r * theta * cos(theta);
// ball->position.y = r * theta * sin(theta);
ball->position = first_ball_pos
+ r * theta * cos(theta) * ux
+ r * theta * sin(theta) * uy;
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
ball->radius = ( i == chain_length - 1 ? 0.6 : 0.3 ) * distance_relaxed;
ball->mass = 4/3.0 * M_PI * pow(ball->radius,3);
ball->contact = false;
}
opt_head_lock = true;
}
void
World::ball_setup_4()
{
}
void
World::ball_setup_5()
{
}
/// Advance Simulation State by delta_t Seconds
//
void
World::time_step_cpu_easy(double delta_t)
{
time_step_count++;
//
/// Compute force and update velocity of each ball.
//
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Skip locked balls.
//
if ( opt_head_lock && i == 0 || opt_tail_lock && i == chain_length - 1 )
{
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
continue;
}
pVect force(0,0,0);
// Gravitational Force
//
force += ball->mass * gravity_accel;
//
// Newton's most famous equation.
// Spring Force from Neighbor Balls
//
for ( int direction: { -1, +1 } )
{
const int n_idx = i + direction; // Compute neighbor index.
// Skip this neighbor if neighbor doesn't exit.
//
if ( n_idx < 0 ) continue;
if ( n_idx == chain_length ) continue;
Ball* const neighbor_ball = &balls[n_idx];
// Construct a normalized (Unit) Vector from ball to neighbor.
//
pNorm ball_to_neighbor( ball->position, neighbor_ball->position );
// Get distance between balls using pNorm member magnitude.
//
const float distance_between_balls = ball_to_neighbor.magnitude;
// Compute by how much the spring is stretched (positive value)
// or compressed (negative value).
//
const float spring_stretch =
distance_between_balls - distance_relaxed;
// Add on the force due to the neighbor_ball.
//
force += opt_spring_constant * spring_stretch * ball_to_neighbor;
// h ( l - l_r ) u_12
//
// Comments above show symbols used in notes.
}
// Update Velocity
//
// This code assumes that force on ball is constant over time
// step. This is clearly wrong when balls are moving with
// respect to each other because the springs are changing
// length. This inaccuracy will make the simulation unstable
// when spring constant is large for the time step.
//
ball->velocity += ( force / ball->mass ) * delta_t;
// Air Resistance
//
const double fs = pow(1+opt_air_resistance,-delta_t);
ball->velocity *= fs;
}
///
/// Update Position of Each Ball
///
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Update Position
//
// Assume that velocity is constant.
//
ball->position += ball->velocity * delta_t;
// Possible Collision with Platform
//
// Skip if collision impossible.
//
if ( !platform_collision_possible(ball->position) ) continue;
if ( ball->position.y >= 0 ) continue;
// Reflect y (vertical) component of velocity, with a reduction
// due to energy lost in the collision.
//
if ( ball->velocity.y < 0 )
ball->velocity.y = - 0.9 * ball->velocity.y;
}
}
void
World::time_step_cpu_full(double delta_t)
{
time_step_count++;
//
/// Compute force and update velocity of each ball.
//
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Skip locked balls.
//
if ( opt_head_lock && i == 0 || opt_tail_lock && i == chain_length - 1 )
{
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
continue;
}
pVect force(0,0,0);
// Gravitational Force
//
force += ball->mass * gravity_accel;
// Spring Force from Neighbor Balls
//
for ( int direction: { -1, +1 } )
{
const int n_idx = i + direction; // Compute neighbor index.
if ( n_idx < 0 ) continue;
if ( n_idx == chain_length ) break;
Ball* const neighbor_ball = &balls[n_idx];
// Construct a normalized (Unit) Vector from ball to neighbor.
//
pNorm ball_to_neighbor( ball->position, neighbor_ball->position );
// Get distance between balls using pNorm member magnitude.
//
const float distance_between_balls = ball_to_neighbor.magnitude;
// Compute by how much the spring is stretched (positive value)
// or compressed (negative value).
//
const float spring_stretch =
distance_between_balls - distance_relaxed;
// Compute the speed of ball towards neighbor_ball.
//
pVect delta_v = neighbor_ball->velocity - ball->velocity;
float delta_s = dot( delta_v, ball_to_neighbor );
// Determine whether spring is gaining energy (whether its length
// is getting further from its relaxed length).
//
const bool gaining_e = ( delta_s > 0.0 ) == ( spring_stretch > 0 );
// Use a smaller spring constant when spring is loosing energy,
// a quick and dirty way of simulating energy loss due to spring
// friction.
//
const float spring_constant =
gaining_e ? opt_spring_constant : opt_spring_constant * 0.7;
force += spring_constant * spring_stretch * ball_to_neighbor;
}
// Update Velocity
//
// This code assumes that force on ball is constant over time
// step. This is clearly wrong when balls are moving with
// respect to each other because the springs are changing
// length. This inaccuracy will make the simulation unstable
// when spring constant is large for the time step.
//
ball->velocity += ( force / ball->mass ) * delta_t;
// Air Resistance
//
const double fs = pow(1+opt_air_resistance,-delta_t);
ball->velocity *= fs;
}
///
/// Update Position of Each Ball
///
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Update Position
//
// Assume that velocity is constant.
//
ball->position += ball->velocity * delta_t;
// Possible Collision with Platform
//
// Skip if collision impossible.
//
if ( !platform_collision_possible(ball->position) ) continue;
if ( ball->position.y >= 0 ) continue;
// Snap ball position to surface.
//
ball->position.y = 0;
// Reflect y (vertical) component of velocity, with a reduction
// due to energy lost in the collision.
//
if ( ball->velocity.y < 0 )
ball->velocity.y = - 0.9 * ball->velocity.y;
}
}
bool
World::platform_collision_possible(pCoor pos)
{
// Assuming no motion in x or z axes.
//
return pos.x >= platform_xmin && pos.x <= platform_xmax
&& pos.z >= platform_zmin && pos.z <= platform_zmax;
}
/// External Modifications to State
//
// These allow the user to play with state while simulation
// running.
// Move the ball.
//
void Ball::translate(pVect amt) {position += amt;}
// Add velocity to the ball.
//
void Ball::push(pVect amt) {velocity += amt;}
// Set the velocity to zero.
//
void Ball::stop() {velocity = pVect(0,0,0); }
// Set the velocity and rotation (not yet supported) to zero.
//
void Ball::freeze() {velocity = pVect(0,0,0); }
void World::balls_translate(pVect amt,int b){balls[b].translate(amt);}
void World::balls_push(pVect amt,int b){balls[b].push(amt);}
void World::balls_translate(pVect amt)
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].translate(amt);}
void World::balls_push(pVect amt)
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].push(amt);}
void World::balls_stop()
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].stop();}
void World::balls_freeze(){balls_stop();}
void
World::frame_callback()
{
// This routine called whenever window needs to be updated.
const double time_now = time_wall_fp();
if ( !opt_pause || opt_single_frame || opt_single_time_step )
{
/// Advance simulation state.
// Amount of time since the user saw the last frame.
//
const double wall_delta_t = time_now - last_frame_wall_time;
const double time_step_duration = 0.0001;
// Compute amount by which to advance simulation state for this frame.
//
const double duration =
opt_single_time_step ? time_step_duration :
opt_single_frame ? 1/30.0 :
wall_delta_t;
const double world_time_target = world_time + duration;
while ( world_time < world_time_target )
{
if ( opt_time_step_easy )
time_step_cpu_easy(time_step_duration);
else
time_step_cpu_full(time_step_duration);
world_time += time_step_duration;
}
// Reset these, just in case they were set.
//
opt_single_frame = opt_single_time_step = false;
}
last_frame_wall_time = time_now;
render();
}
int
main(int argv, char **argc)
{
pOpenGL_Helper popengl_helper(argv,argc);
World world(popengl_helper);
popengl_helper.rate_set(30);
popengl_helper.display_cb_set(world.frame_callback_w,&world);
}
// Desired position of first ball.
//
pCoor first_ball_pos(13.4,17.8,-9.2);
pVect peu(first_ball_pos,eye_location);
pNorm pe = peu;
pNorm uz = pe + pVect(0,1,0);
pNorm ux = cross( pVect(0,1,0), uz );
pNorm uy = cross( uz, ux );
float r = 10;
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
double theta = 2 * M_PI * i / chain_length;
// ball->position.x = r * theta * cos(theta);
// ball->position.y = r * theta * sin(theta);
ball->position = first_ball_pos
+ r * theta * cos(theta) * ux
+ r * theta * sin(theta) * uy;
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
ball->radius = ( i == chain_length - 1 ? 0.6 : 0.3 ) * distance_relaxed;
ball->mass = 4/3.0 * M_PI * pow(ball->radius,3);
ball->contact = false;
}
opt_head_lock = true;
}
void
World::ball_setup_4()
{
}
void
World::ball_setup_5()
{
}
/// Advance Simulation State by delta_t Seconds
//
void
World::time_step_cpu_easy(double delta_t)
{
time_step_count++;
//
/// Compute force and update velocity of each ball.
//
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Skip locked balls.
//
if ( opt_head_lock && i == 0 || opt_tail_lock && i == chain_length - 1 )
{
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
continue;
}
pVect force(0,0,0);
// Gravitational Force
//
force += ball->mass * gravity_accel;
//
// Newton's most famous equation.
// Spring Force from Neighbor Balls
//
for ( int direction: { -1, +1 } )
{
const int n_idx = i + direction; // Compute neighbor index.
// Skip this neighbor if neighbor doesn't exit.
//
if ( n_idx < 0 ) continue;
if ( n_idx == chain_length ) continue;
Ball* const neighbor_ball = &balls[n_idx];
// Construct a normalized (Unit) Vector from ball to neighbor.
//
pNorm ball_to_neighbor( ball->position, neighbor_ball->position );
// Get distance between balls using pNorm member magnitude.
//
const float distance_between_balls = ball_to_neighbor.magnitude;
// Compute by how much the spring is stretched (positive value)
// or compressed (negative value).
//
const float spring_stretch =
distance_between_balls - distance_relaxed;
// Add on the force due to the neighbor_ball.
//
force += opt_spring_constant * spring_stretch * ball_to_neighbor;
// h ( l - l_r ) u_12
//
// Comments above show symbols used in notes.
}
// Update Velocity
//
// This code assumes that force on ball is constant over time
// step. This is clearly wrong when balls are moving with
// respect to each other because the springs are changing
// length. This inaccuracy will make the simulation unstable
// when spring constant is large for the time step.
//
ball->velocity += ( force / ball->mass ) * delta_t;
// Air Resistance
//
const double fs = pow(1+opt_air_resistance,-delta_t);
ball->velocity *= fs;
}
///
/// Update Position of Each Ball
///
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Update Position
//
// Assume that velocity is constant.
//
ball->position += ball->velocity * delta_t;
// Possible Collision with Platform
//
// Skip if collision impossible.
//
if ( !platform_collision_possible(ball->position) ) continue;
if ( ball->position.y >= 0 ) continue;
// Reflect y (vertical) component of velocity, with a reduction
// due to energy lost in the collision.
//
if ( ball->velocity.y < 0 )
ball->velocity.y = - 0.9 * ball->velocity.y;
}
}
void
World::time_step_cpu_full(double delta_t)
{
time_step_count++;
//
/// Compute force and update velocity of each ball.
//
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Skip locked balls.
//
if ( opt_head_lock && i == 0 || opt_tail_lock && i == chain_length - 1 )
{
ball->velocity = pVect(0,0,0);
continue;
}
pVect force(0,0,0);
// Gravitational Force
//
force += ball->mass * gravity_accel;
// Spring Force from Neighbor Balls
//
for ( int direction: { -1, +1 } )
{
const int n_idx = i + direction; // Compute neighbor index.
if ( n_idx < 0 ) continue;
if ( n_idx == chain_length ) break;
Ball* const neighbor_ball = &balls[n_idx];
// Construct a normalized (Unit) Vector from ball to neighbor.
//
pNorm ball_to_neighbor( ball->position, neighbor_ball->position );
// Get distance between balls using pNorm member magnitude.
//
const float distance_between_balls = ball_to_neighbor.magnitude;
// Compute by how much the spring is stretched (positive value)
// or compressed (negative value).
//
const float spring_stretch =
distance_between_balls - distance_relaxed;
// Compute the speed of ball towards neighbor_ball.
//
pVect delta_v = neighbor_ball->velocity - ball->velocity;
float delta_s = dot( delta_v, ball_to_neighbor );
// Determine whether spring is gaining energy (whether its length
// is getting further from its relaxed length).
//
const bool gaining_e = ( delta_s > 0.0 ) == ( spring_stretch > 0 );
// Use a smaller spring constant when spring is loosing energy,
// a quick and dirty way of simulating energy loss due to spring
// friction.
//
const float spring_constant =
gaining_e ? opt_spring_constant : opt_spring_constant * 0.7;
force += spring_constant * spring_stretch * ball_to_neighbor;
}
// Update Velocity
//
// This code assumes that force on ball is constant over time
// step. This is clearly wrong when balls are moving with
// respect to each other because the springs are changing
// length. This inaccuracy will make the simulation unstable
// when spring constant is large for the time step.
//
ball->velocity += ( force / ball->mass ) * delta_t;
// Air Resistance
//
const double fs = pow(1+opt_air_resistance,-delta_t);
ball->velocity *= fs;
}
///
/// Update Position of Each Ball
///
for ( int i=0; i<chain_length; i++ )
{
Ball* const ball = &balls[i];
// Update Position
//
// Assume that velocity is constant.
//
ball->position += ball->velocity * delta_t;
// Possible Collision with Platform
//
// Skip if collision impossible.
//
if ( !platform_collision_possible(ball->position) ) continue;
if ( ball->position.y >= 0 ) continue;
// Snap ball position to surface.
//
ball->position.y = 0;
// Reflect y (vertical) component of velocity, with a reduction
// due to energy lost in the collision.
//
if ( ball->velocity.y < 0 )
ball->velocity.y = - 0.9 * ball->velocity.y;
}
}
bool
World::platform_collision_possible(pCoor pos)
{
// Assuming no motion in x or z axes.
//
return pos.x >= platform_xmin && pos.x <= platform_xmax
&& pos.z >= platform_zmin && pos.z <= platform_zmax;
}
/// External Modifications to State
//
// These allow the user to play with state while simulation
// running.
// Move the ball.
//
void Ball::translate(pVect amt) {position += amt;}
// Add velocity to the ball.
//
void Ball::push(pVect amt) {velocity += amt;}
// Set the velocity to zero.
//
void Ball::stop() {velocity = pVect(0,0,0); }
// Set the velocity and rotation (not yet supported) to zero.
//
void Ball::freeze() {velocity = pVect(0,0,0); }
void World::balls_translate(pVect amt,int b){balls[b].translate(amt);}
void World::balls_push(pVect amt,int b){balls[b].push(amt);}
void World::balls_translate(pVect amt)
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].translate(amt);}
void World::balls_push(pVect amt)
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].push(amt);}
void World::balls_stop()
{ for(int i=0;i<chain_length;i++)balls[i].stop();}
void World::balls_freeze(){balls_stop();}
void
World::frame_callback()
{
// This routine called whenever window needs to be updated.
const double time_now = time_wall_fp();
if ( !opt_pause || opt_single_frame || opt_single_time_step )
{
/// Advance simulation state.
// Amount of time since the user saw the last frame.
//
const double wall_delta_t = time_now - last_frame_wall_time;
const double time_step_duration = 0.0001;
// Compute amount by which to advance simulation state for this frame.
//
const double duration =
opt_single_time_step ? time_step_duration :
opt_single_frame ? 1/30.0 :
wall_delta_t;
const double world_time_target = world_time + duration;
while ( world_time < world_time_target )
{
if ( opt_time_step_easy )
time_step_cpu_easy(time_step_duration);
else
time_step_cpu_full(time_step_duration);
world_time += time_step_duration;
}
// Reset these, just in case they were set.
//
opt_single_frame = opt_single_time_step = false;
}
last_frame_wall_time = time_now;
render();
}
int
main(int argv, char **argc)
{
pOpenGL_Helper popengl_helper(argv,argc);
World world(popengl_helper);
popengl_helper.rate_set(30);
popengl_helper.display_cb_set(world.frame_callback_w,&world);
}